User:Jukeboksi/Wiki.study/Natural therapeutics: Difference between revisions
imported>Jukeboksi (→Terpenes in cannabis: + 'Why terpenes are becoming more important than THC', a 2019 articleon the Spokesman.com) |
imported>Jukeboksi (→Cannabis: + == Making cannabinoids with yeasts == + Scientists have figured out how to splice the DNA of yeasts, so that they produce cannabinoids. + <ref name="GlobalHealthTimes2019">) |
||
| Line 210: | Line 210: | ||
* [http://www.spokesman.com/stories/2019/mar/01/why-terpenes/ 'Why terpenes are becoming more important than THC'], a 2019 articleon the Spokesman.com | * [http://www.spokesman.com/stories/2019/mar/01/why-terpenes/ 'Why terpenes are becoming more important than THC'], a 2019 articleon the Spokesman.com | ||
---- | ---- | ||
== Making cannabinoids with yeasts == | |||
Scientists have figured out how to splice the DNA of yeasts, so that they produce cannabinoids.<ref name="GlobalHealthTimes2019">http://globalhealthtimes.com/2019/03/06/scientists-are-making-thc-and-cbd-in-a-lab-without-growing/</ref> | |||
---- | |||
== Synthetic cannabinoids == | == Synthetic cannabinoids == | ||
'''[[w:Synthetic cannabinoids|Synthetic cannabinoids]]''' are a class of molecules that [[w:Binding affinity|bind]] to [[w:cannabinoid receptor|cannabinoid receptor]]s in the body — the same receptors to which [[w:Tetrahydrocannabinol|THC]] and [[w:Cannabidiol|CBD]] attach – which are [[w:cannabinoid|cannabinoid]]s in [[w:cannabis|cannabis]] plants. (Wikipedia) | '''[[w:Synthetic cannabinoids|Synthetic cannabinoids]]''' are a class of molecules that [[w:Binding affinity|bind]] to [[w:cannabinoid receptor|cannabinoid receptor]]s in the body — the same receptors to which [[w:Tetrahydrocannabinol|THC]] and [[w:Cannabidiol|CBD]] attach – which are [[w:cannabinoid|cannabinoid]]s in [[w:cannabis|cannabis]] plants. (Wikipedia) | ||
Revision as of 17:35, 28 May 2019
Nature provides us with many healing agents but these are often pushed to the periphery of public knowledge to ensure big pharma profits.
Blackberries

Blackberries kill antibiotic resistant staphylococcus aureus bacteria[1]. Irish teen awarded prize for discovery.[2]
Boswellia - Frankincense

Boswellia is a genus of trees in the order Sapindales, known for their fragrant resin. The biblical incense w:frankincense was an extract from the resin of the tree Boswellia sacra, and is now produced also from B. frereana. (Wikipedia)
- 'Frankincense oil kills cancer cells while boosting the immune system, studies show' a 2016 article by Dr. Josh Axe at healthy-holistic-living.com
- 'Frankincense found to outperform chemo in killing Ovarian Cancer cells' 2019 popular article on GetHolisticHealth.com
Cannabis
Cannabis is the oldest and most versatile medicine known to humankind.
Cannabis sativa and Cannabis indica are the main cannabis variants though most strains are mixes of these. A third cannabis line is the Cannabis ruderalis, a rugged northern cannabis that has adapted to flower even under northern long summer days.
The endocannabinoid system
Main article in wikipedia Endocannabinoid system
Endocannabinoids are synthesized by our own bodies from Arachidonic acid, an essential polyunsaturated Omega-6 fatty acid[3].
Articles about the endocannabinoid system
- 'Modulating the endocannabinoid system in human health and disease--successes and failures', a 2013 scientific article
- 'Care and Feeding of the Endocannabinoid System: A Systematic Review of Potential Clinical Interventions that Upregulate the Endocannabinoid System', a 2014 article
- 'Fatty Acid Modulation of the Endocannabinoid System and the Effect on Food Intake and Metabolism', a 2013 article
- 'The endocannabinoid system in pain and inflammation: Its relevance to rheumatic disease', a 2017 article
- 'Endocannabinoid system: Role in depression, reward and pain control' (Review), a 2016 article
- 'Care and Feeding of the Endocannabinoid System: A Systematic Review of Potential Clinical Interventions that Upregulate the Endocannabinoid System', a 2014 systematic review
- 'Fatty Acid Modulation of the Endocannabinoid System and the Effect on Food Intake and Metabolism', a 2013 study
- 'The endocannabinoid system in pain and inflammation: Its relevance to rheumatic disease', a 2017 article
- 'Potential for endocannabinoid system modulation in ocular pain and inflammation: filling the gaps in current pharmacological options', a 2018 article
The endocannabinoid receptors
Human body contains 2 types of endocannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2.
CB1 receptors
CB1 receptors predominantly located in the nervous system, connective tissues, gonads, glands, and organs[4].
CB2 receptors
CB2 receptors, primarily found in the immune system and also present in the spleen, liver, heart, kidneys, bones, blood vessels, lymph cells, endocrine glands, and reproductive organs[4].
Endocannabinoids
The two main endocannabinoids are Anandamide and 2-AG.
Anandamide
Anandamide was discovered in 1992 and it binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors. The name comes from the Sanskrit word 'Ananda' meaning 'bliss' and amide from its chemistry.
It has been referred to as the endocannabinoid version of THC.
Synthesis of Anandamide: Arachidonic acid -> Phosphatidylethanolamide + N-Acyltransferase -> N-arachidonoyl phosphatidylethanolamine + Phospholipase D -> Anandamide[5]
2-AG
2-Arachidonoylglycerol aka. 2-AG was discovered in 1994-1995.
Synthesis of 2-AG: Arachidonic acid -> Phosphatidylinositol + Phospholipase Cs -> w:Diacylglycerol + Diacylglycerol lipase -> 2-AG[5]
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine
N-Arachidonoyl dopamine discovered in 2000.
2-Arachidonyl glyceryl ether
2-Arachidonyl glyceryl ether discovered in 2001.
Virodhamine
Virodhamine discovered in 2002
Lysophosphatidylinositol
Lysophosphatidylinositol is a contender to be the 6th endocannabinoid.
Further reading on the endocannabinoid system
- Endocannabinoids – Beyond the Brain is a good 2017 article on the Hemp Edification blog] adapted from Your Body Is Teeming with Weed Receptors, a 2017 article on the website the-scientist.com and Endocannabinoids in the Groove, a 2017 article on the website the-scientist.com
- 'Introduction to the Endocannabinoid System' at NORML (.org)
- http://profofpot.com/endocannabinoid-receptors/
Phytocannabinoids

Many people may know the 2 most prevalent phytocannabinoids, THC and CBD.
Studies about phytocannabinoids
- 'Non-psychotropic plant cannabinoids: new therapeutic opportunities from an ancient herb.', a 2009 article
Links about phytocannabinoids
List of known phytocannabinoids from Wikipedia:
- THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol)
- THCA (Tetrahydrocannbinolic acid)
- CBD (Cannabidiol)
- CBDA (Cannabidiolic Acid)
- CBN (Cannabinol)
- CBG (Cannabigerol)
- CBC (Cannabichromene)
- CBL (Cannabicyclol)
- CBV (Cannabivarin)
- THCV (Tetrahydrocannabivarin)
- CBDV (Cannabidivarin)
- CBCV (Cannabichromevarin)
- CBGV (Cannabigerovarin)
- CBGM (Cannabigerol Monomethyl Ether)
- CBE (Cannabielsoin)
- CBT (Cannabicitran)
THC
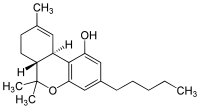
Tetrahydrocannabinol was found in 1964[7] and it is the main psychoactive compound that brings the 'high' most recreational users are chasing.
THCA
Tetrahydrocannabinolic acid THCA is the what cannabis plants produce to fend off insects from harming it. In pure form THCA is a clear translucent crystalline of white color.
THC is produced from the raw THCA by a process called decarboxylation. Basically means to heat the stuff over certain temperature.
THCA found in raw marijuana apparently has some health enhancing properties. The issue is being researched.
- https://herb.co/news/health/raw-weed-benefits/
- https://herb.co/learn/eat-raw-weed-marijuana/
- https://thefreshtoast.com/cannabis/marijuanas-thc-a-as-an-anti-inflammatory-and-neuro-protectant/
CBD
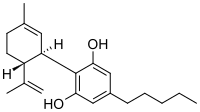
Cannabidiol was isolated and identified from Cannabis sativa in 1940[7]. CBD is not psychoactive and it has the most medical applications of all phytocannabinoids.
“Cannabidiol has little affinity for CB1 and CB2 receptors but acts as an indirect antagonist of cannabinoid agonists.[8]”
- Hightimes in detail piece on CBD
- Leafly lists strains high in CBD
- Piece on CBD as anti-pain agent (contains ads)
- WHO preliminary report on CBD
CBDA
Cannabidiolic Acid is the raw form. Decarboxylating CBDA yields CBD.
CBN
Cannabinol is a sleeping aid and has also other therapeutic qualities.
- https://www.massroots.com/learn/cannabinol-cbn-cannabinoid/
- https://www.medicaljane.com/2013/08/19/cannabinol-cbn-will-put-you-to-bed/
CBG
“Cannabigerol has been shown to promote apoptosis in cancer cells and inhibit tumor growth in mice. It acts as an α2-adrenergic receptor agonist, 5-HT1A receptor antagonist, and CB1 receptor antagonist.[9] It also binds to the CB2 receptor.[9]”
Links about CBG
CBC
CBL
CBV
THCV
Tetrahydrocannabivarin can be used to inhibit appetite.
Links about THCV
CBDV
CBCV
Cannabichromevarin
CBGV
Cannabigerovarin
CBGM
Cannabigerol Monomethyl Ether
CBE
Cannabielsoin
CBT
Cannabicitran
Terpenes in cannabis
Terpenes are a large and diverse class of organic compounds, produced by a variety of plants, particularly conifers, and by some w:insects.[10]
Links about terpenes found in cannabis
- '15 terpenes in cannabis explained', a 2018 article by CannaCon.org
- 'Terpenes' by Fundación CANNA, a non-profit organization dedicated to scientific studies and cannabis testing
- 'Why terpenes are becoming more important than THC', a 2019 articleon the Spokesman.com
Making cannabinoids with yeasts
Scientists have figured out how to splice the DNA of yeasts, so that they produce cannabinoids.[11]
Synthetic cannabinoids
Synthetic cannabinoids are a class of molecules that bind to cannabinoid receptors in the body — the same receptors to which THC and CBD attach – which are cannabinoids in cannabis plants. (Wikipedia)
Word of caution: Many synthetic cannabinoids are dangerous and should not be administered by others than medical professionals.
- List of synthetic cannabinoids on Wikipedia
- Structural scheduling of synthetic cannabinoids on Wikipedia
ACEA
Arachidonyl-2'-chloroethylamide (ACEA) is a synthetic agonist of the CB1 receptor.
Other plants that contain compounds that are active in cannabinoid receptors
- Echinacea contains N-alkylamides, that function via cannabimemetics to provide immune-boosting and is also used to relieve anxiety, fatigue, migraines and arthritis.[12]
- Black pepper contains high levels of the terpene called β-caryophyllene (BCP). BCP functions as a cannabinoid, and has a binding affinity with the CB2 receptor.[12]
- Flax (linen) seeds produce cannabinoid-like compounds very similar to CBD.[12]
- Cacao contains lots of magnesium, but also "happy-brain" chemicals like theobromine, phenethylamine, tryptophan, and anandamide. Cacao affects the endocannabinoid system by deactivating the enzyme called FAAH. This enzyme breaks down the endocannabinoid known as anandamide.[12]
- Black truffles contain anandamide.[12]
- Helichrysum umbraculigerum contains cannabigerol (CBG).[12]
- Rhododendron anthopogonoides (Chinese Labrador) contains anthopogocyclolic acid and anthopogochromenic acid and five related compounds known as synthetic analogues of cannabinoids: cannabichromene (CBC) type, cannabicyclol (CBL) type and cannabicitran (CBT) type, have been isolated together with geranyl orsellinic acid. [12]
- Liverwort contains Perrottetinene, a cannabinoid similar to THC.[13][12]
- https://herb.co/learn/non-marijuana-plants-contain-cannabinoids/
- https://livelovefruit.com/8-non-marijuana-plants-contain-cannabinoids/
- https://www.marijuana.com/news/2017/05/9-plants-that-contain-therapeutic-cannabinoids/
Cannabis therapeutics


Cannabis can be applied to treat a wide assortment of illnesses. In this case it is called medical cannabis.
Due to the inbuilt default to always take the safe route and also to backup the back of your fellow MD colleague the Wikipedia does not yield the right infos on how useful and versatile a medication cannabis is.
Research has been held back by arcane laws even as cannabis is the oldest medicine known to man and it should be gladly appreciated and not outlawed because of big pharma interests.
Medical cannabis research and information organizations
- International Association for Cannabinoid Medicines is also available in German, French, Dutch, Spanish, Portuguese and Italian
- The Canadian Consortium for the Investigation of Cannabinoids is a Canadian non-profit organization
- The Center for Medicinal Cannabis Research at the University of California
- Centre for Medicinal Cannabis Research and Innovation by the govt of New South Wales
External links about cannabis as medicine
- http://www.calgarycmmc.com/ a large compendium on medical cannabis sorted alphabetically by ailment.
- http://www.cannabisconnections.tk/2018/03/700-medicinal-uses-of-cannabis-sorted.html
- http://expand-your-consciousness.com/100-scientific-studies-agree-cannabis-annihilates-cancer/ about 100 nih.gov studies linked some cases briefly described.
- https://healer.com/ - a website by Dr. Dustin Sulak D.O. - a renowned integrative medicine physician based in Maine, whose practice balances the principles of osteopathy, mind-body medicine and medical cannabis.
- Harvard Health Blog article on medical cannabis is naturally very reserved about not raising too much hopes
- 71 medical uses of cannabis compiled by LearnGreenFlower.com
- http://medicalcannabisreport.com/700-medicinal-uses-of-cannabis-sorted-by-disease/ (.pdf from 2012 downloadable from the linked page)
Literature about cannabis as a medicine
- BPJ Volume 163, Issue 7 - 'Special Issue:Cannabinoids in Biology and Medicine, Part I.' a 2011 special issue of w:British Journal of Pharmacology.
- MARIJUANA AS MEDICINE? - The Science Beyond the Controversy (full book online), a somewhat skeptical and reserved book published in 2000 that you can read online from The National Academies Press.
- MARIHUANA: THE FORBIDDEN MEDICINE (excerpts from the book online), a 1997 book by Lester Grinspoon, M.D and James Bakalar, J.D
Anecdotal testimonies about medical cannabis
- Anecdotal testimonies on medical cannabis at calgarymmc.com
- Anecdotal testimonies on medical cannabis at rxmarijuana.com
Alzheimer's disease and cannabis
Cannabis has been found to be beneficial for Alzheimer's sufferers. Especially true this is for THC which inhibits the formulation of toxic beta amyloid protein plaque on braincells which causes Alzheimer's disease.
Scientific research about Alzheimer's and cannabis
- 'Cannabis Therapeutics and the Future of Neurology: Cannabis and Alzheimer Disease (AD)', a 2018 perspectives article
- News (2016): "Cannabinoids remove plaque-forming Alzheimer’s proteins from brain cells" @ salk.edu - Preliminary lab studies at the Salk Institute find THC reduces beta amyloid proteins in human neurons
Links about Alzheimer's disease and cannabis
- Wikipedia article on Alzheimer's disease research has only a few words about cannabis therapeutics and those are very sceptical.
Asthma and cannabis
- Extensive compendium of research about asthma and cannabis compiled by calgarycmmc.com
- https://herb.co/learn/cannabis-asthama/
- 'THC Makes Cannabis Ideal for Treating Asthma, Study Shows' at Waking Times (2016)
Autism and cannabis
- Extensive compendium of research about autism and cannabis compiled by calgarycmmc.com
- http://www.newsweek.com/2018/02/23/really-good-weed-why-cannabis-may-be-worlds-most-effective-remedy-core-806758.html
- https://www.whatiscbd.com/cbd-for-autism/
Autoimmune diseases and cannabis
Cannabis helps with many autoimmune diseases due to its anti-inflammatory and other properties.
Links about autoimmune diseases and cannabis
Rheumatoid arthritis and cannabis
Cannabis helps with Rheumatoid arthritis.
Studies about rheumatic diseases and cannabis
- 'The endocannabinoid system in pain and inflammation: Its relevance to rheumatic disease', a 2017 article
Links about Rheumatoid arthritis and cannabis
- http://ehealthmagz.com/2018/10/29/cannabis-could-be-reversing-damage-to-arthritic-joints/
- https://herb.co/news/health/greenlight-medicines-cannabis-arthritis/
- https://livelovefruit.com/cannabis-for-arthritis/
Lupus and cannabis
Cannabis helps with Systemic lupus erythematosus
Coeliac disease and cannabis
Cannabis helps with Coeliac disease.
Psoriasis and cannabis
You could also be looking for dermatitis, also known as eczema.
Cannabis helps with Psoriasis and when applied externally.
- https://herb.co/learn/cbd-lotion-psoriasis/
- https://herb.co/guides/cbd-oil-psoriasis-eczema/
- https://hightimes.com/health/treat-psoriasis-with-cannabis/
Type 1 diabetes and cannabis
Cancers and cannabis
Key things everyone needs to know about cancers and cannabis
Warning: Smoking the cannabis as the method of cannabinoid delivery the smoke contains quite a few carcinogenic substances i.e. cancer inducing substances. See the section administering cannabis for alternatives to smoking it.
Internet is rife with stories about winning the battle against cancer with the help of phytocannabinoids. What does the science say?
Cannabis is...
- Anti-proliferative - cannabis is against tumor growth [14]
- Anti-metastatic - cannabis is against cancer spreading to other parts in the body because of metastatic activity[14]
- Anti-angiogenetic - cannabis is against new blood vein growth to tumor[14]
- Apoptotic - cannabis causes cancer cells to programmedly kill themselves via Apoptosis. [14]
- Pain relief - cannabis works very well against the somatic and nonsomatic pains brought on by cancer.
- Appetite stimulator - cannabis helps maintain a good appetite.
- Anti-nauseatic - cannabis helps with the chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting if you receive chemotherapy. World's first study of cannabis for chemotherapy's negative effects is underway in Australia. [15] [16]
Phytocannabinoids are harmless to healthy cannabinoid receptor containing cells.
- Everything You Need To Know About Cannabis And Cancer Treatment, a 2017 article at herb.co
- These Are The 4 Ways Cannabis Kills Cancer, a 2016 article at herb.co
Links about cannabis and cancer in general
"Official" information
- National Cancer Institute of USA on cancers and cannabis (health professional version)
- National Cancer Institute of USA on cancers and cannabis (patient version)
Cannabis and cancers advocacy
- A compendium of research regarding cancers and cannabis at calgarycmmc.com
- Cannabis Research A to Z, the letter 'C' at calgarycmmc.com
- Exposing The Truth: Links with abstracts to 123 scientific articles on cannabis and cancers
- http://www.healedbycannabis.com/ Healed by Cannabis website] by a cancer survivor David Triplett who healed his skin cancer with cannabis oil
- https://herb.co/news/health/cancer-institute-finally-admits-marijuana-kills-cancer/
- https://herb.co/news/health/us-govt-admits-marijuana-kills-cancer-cells/
Testimonies about cannabis and cancer
Cancer surviving cases with cannabis
Scientific studies and papers about cannabis and cancers in general
- "Anticancer mechanisms of cannabinoids", a 2016 paper published in Current Oncology
- "Cannabidiol as potential anticancer drug",a 2017 paper published in the British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology
Learn from videos by experts in phytocannabinoid treatment of cancers
People:
- Dr. Cristina Sánchez is a molecular biology research scientist who did her doctorate on cannabinoids and cancers. She is a leader in researching the anti-cancer qualities of cannabinoids. She works at the w:Complutense University of Madrid
- Dr. Manuel Guzmán also works as a molecular biology researcher on researching the potential of cannabis as a cancer medication in the Complutense University of Madrid.
- Dr. Wai Liu works on researching medical cannabis for cancer (among other things) at the w:St George's, University of London.
Videos
- Dr. Cristina Sanchez interview where she expains how apoptosis makes cancer cells kill themselves
- Dr. Cristina Sanchez on how cannabinoids work against cancers
- Dr. Cristina Sanchez at Cannafest Prague 2015
- Dr. Cristina Sanchez lecture in Australia (no slideshow shots, sorry)
See also: Cancers and turmeric (intra-article link)
Brain cancer and cannabis
A glioma is a type of tumor that starts in the glial cells of the brain or the spine. (Wikipedia) A blastoma is a type of cancer, more common in children, that is caused by malignancies in precursor cells. (Wikipedia)
Glioblastoma is the most aggressive form of brain cancer, but it may potentially be treated with cannabis.[17]
In 2018 Insys Therapeutics announced the the FDA has given CBD an orphan drug designation (ODD) to CBD for treating gliomas.[18]
Studies about brain tumors and cannabis
- 'Cannabis Therapeutics and the Future of Neurology: Cannabis and Brain Tumors', a 2018 perspective article
Links about brain cancer and cannabis
- Extensive compendium of research about brain cancer and cannabis at calgarycmmc.com
- https://herb.co/news/health/cannabis-treat-brain-cancer/
- https://herb.co/news/health/taylor-rehmeyer/
Breast cancer and cannabis
Cervical cancer and cannabis
Colon cancer and cannabis
Langerhans cell sarcoma
Langerhans cell sarcoma is extremely rare.
Leukemia and cannabis
There are 2 main types of Leukemia:
- Myeloid leukemia (of the bone marrow)
- Lymphoid leukemia (of the lymphatic node)
Links about Lympoid and Myeloid leukemia and cannabis
- Dronabinol (synthetic THC) has preferential antileukemic activity in acute lymphoblastic and myeloid leukemia with lymphoid differentiation patterns
- Enhancing the Activity of Cannabidiol and Other Cannabinoids In Vitro Through Modifications to Drug Combinations and Treatment Schedules, a 2013 study published in the journal Anticancer Research
Links about Lymphoid leukemia and cannabis
- https://ocgreenrelief.org/medical-marijuana/cannabis-oil-acute-leukemia-2
- http://truemedmd.com/2014/06/cannabis-oil-acute-leukemia/
Links about Myeloid leukemia and cannabis
- Extensive compendium of reasearch on leukemia and cannabis at calgarycmmc.com
- http://www.leafscience.com/2013/10/14/cannabinoids-destroy-leukemia-cells-new-study-finds/
- https://medijane.co.za/disease-index/will-marijuana-cure-cancer/acute-myeloid-leukemia-aml-cannabis/
Liver cancer and cannabis
Lung cancer and cannabis
Laboratory and mice studies seem to indicate that THC can slow down the growth of lung cancer tumours from growing by binding to the same receptors as epidermal growth factor (EGF): the epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR).
- Extensive compendium of reasearch on lung cancer and cannabis at calgarycmmc.com
- An article on a 2007 study on THC against lung cancer on sciencedaily.com
- Study: "Δ-9 Tetrahydrocannabinol inhibits growth and metastasis of lung cancer." presented at the 2007 AACR Annual Meeting
Lung cancer and cannabis in the media
- Marijuana Compound May Fight Lung Cancer at abcnews.go.com
- Patient taking CBD oil found to have significant shrinking of the tumor (2019 article)
Lymphoma
Hodgkin's lymphoma is a type of lymphoma in which cancer originates from a specific type of white blood cells called lymphocytes. (Wikipedia)
- Extensive compendium of reasearch on lymphoma and cannabis at calgarycmmc.com
- https://herb.co/news/health/hodgkins-lymphoma-cannabis/
Oral cancer and cannabis
Osteosarcoma
w:Osteosarcoma is a bone cancer.
Ovarian cancer and cannabis
Pancreatic cancer and cannabis
- Medical cannabis extract could help pancreatic cancer patients live longer, early study suggests an 2019 article in the Independent
Prostate cancer and cannabis
Cannabis helps with prostate cancer.
- Extensive compendium of research on prostate cancer and cannabis at calgarycmmc.com
- https://cannabishealthradio.com/blog/2017/09/18/episode-217-his-incurable-prostate-cancer-has-been-cleared-with-the-use-of-cannabis-oil/
Skin cancer and cannabis
- Extensive compendium of research on skin cancer and cannabis at calgarycmmc.com
- https://www.theroc.us/researchlibrary/Differential%20role%20of%20cannabinoids%20in%20the%20pathogenesis%20of%20skin%20cancer.pdf
Melanoma and cannabis
- Extensive compendium of research on melanoma and cannabis at calgarycmmc.com
- https://herb.co/learn/skin-cancer/
Testicular cancer and cannabis
Thyroid cancer and cannabis
Crohn's disease and cannabis
Study shows THC helps with Crohn's disease.
- 'Medical Cannabis' by the Gastrointestinal Society (of Canada)
- Extensive compendium of research about Crohn's disease and cannabis compiled by calgarycmmc.com
- 'Cannabis relieves symptoms in Crohn's disease', a 2018 article at MedicalNewsToday.com
- 'Crohn's Patients See 65% Remisson in Placebo/Cannabis Clinical Trial', 2019 reporting by RXLeaf.com
- https://theheartysoul.com/cannabis-crohns-disease-treatment-remission/
Epilepsy and cannabis
Cannabis can be used to treat epilepsy.
Studies about epilepsies and cannabis
Links about epilepsies and cannabis
- https://www.dailymail.co.uk/health/article-6302465/Epileptic-boy-nearly-sectioned-attends-school-day-cannabis-oil.html
- http://sorendreier.com/boy-with-100-seizures-a-day-now-has-none-after-taking-cannabis-oil/
- http://www.rosintech.com/how-cannabis-concentrates-can-help-those-with-epilepsy/
Dermatitis
Dermatitis, also known as eczema, is a group of diseases that results in inflammation of the skin that includes atopic dermatitis, allergic contact dermatitis, irritant contact dermatitis and stasis dermatitis. (Adapted from Wikipedia)
- Extensive compendium of research about dermatitis and cannabis compiled by calgarycmmc.com
- https://herb.co/guides/cbd-oil-psoriasis-eczema/
Migraines and cannabis
It has been suggested that clinical endocannabinoid deficiency syndrome (CEDS) may be causing migraines. Many studies found medical cannabis as an effective prophylaxis against migraine attacks, especially the high CBD strains.
- Extensive compendium of research about migraines and cannabis compiled by calgarycmmc.com
- CBD Testers article on treating migraines with medical cannabis and link to the study 'Effects of Medical Marijuana on Migraine Headache Frequency in an Adult Population' at PubMed that the article is talking about.
- Abstracts of studies on migraines and medical cannabis at migrainebuds.com
- https://www.rxleaf.com/migraine-relief
Pain treatment with cannabis
“You just don't feel like thinking about the pain.”
“There is more to it than that.”
Cannabis is anti-inflammatory which helps relieve some of the pain. Pain is a signal of inflammation so counter-acting inflammation causing things cannabis naturally helps lower the pain.
Parkinsons disease and cannabis
Scientific studies on the issue of Parkinsons and cannabinoids
- 'Cannabis Therapeutics and the Future of Neurology: Cannabis and Parkinson Disease (PD), a 2018 perspective article
- A 2016 scientific review article: Marijuana Compounds: A Nonconventional Approach to Parkinson's Disease Therapy
Compendiums of research
Articles in media
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/abbierosner/2019/02/26/cannabis-for-parkinsons-and-alzheimers-diseases-an-interview-with-dr-ethan-russo/#10fc5c765dd6
- https://herb.co/marijuana/news/cannabis-and-parkinsons-disease
- https://tonic.vice.com/en_us/article/paykwm/weed-could-help-prevent-certain-brain-diseases
- https://scienceofparkinsons.com/2016/09/25/cannabis/
Non-somatic issues with cannabis
Cannabis can help with various non-somatic problems such as psychiatry, depression and PTSD.
Depression and cannabis
Psychosis and cannabis
Studies about psychosis and cannabis
- 'Opposite effects of delta-9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol on human brain function and psychopathology.' - a 2010 study published in w:Neuropsychopharmacology (journal)
- 'Effect of Cannabidiol on Medial Temporal, Midbrain, and Striatal Dysfunction in People at Clinical High Risk of Psychosis', a 2018 randomized controlled trial
Articles about psychosis and cannabis
- 'Harvard Study Proves Cannabis Does Not Cause Schizophrenia' a 2019 article at CannabisActivismNow.com
- 'Psychosis: Cannabis extract normalizes brain function' a 2018 article at MedicalNewsToday.com refers to studies regarding CBD having an anti-psychotic effect
- 'Brain scans show how cannabis extract may help people with psychosis' (2018) article at TheGuardian.com
PTSD and cannabis
Studies about medical cannabis for PTSD
- First ever clinical trial of medical marijuana for PTSD sponsored by w:Multidisciplinary Association for Psychedelic Studies to start at the Scottsdale Research Institute in Arizona (2016) Update on phase 2 of the study (2017). High Times reports the clinical trial completed in 2019 results coming later on.
Links about medical cannabis for PTSD
- 'Brain-imaging study links cannabinoid receptors to post-traumatic stress disorder: First pharmaceutical treatment for PTSD within reach' (2013) at ScienceDaily.com
- Extensive compendium of research about PTSD and cannabis compiled by calgarycmmc.com
- https://www.leafly.com/news/health/cannabis-and-post-traumatic-stress-disorder-ptsd
- https://www.nbcbayarea.com/news/local/Marijuana-May-Cure-PTSD-208900021.html
Sclerosis
“In medicine, sclerosis is the stiffening of a structure, usually caused by a replacement of the normal organ-specific tissue with connective tissue.”
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and cannabis
Cannabis helps with Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) also known as Lou Gehrig's disease and motor neurone disease (MND).
Multiple sclerosis (MS) and cannabis
Cannabis is very good against Multiple sclerosis. Prince Charles knew of this way back in 1998[19].
- Extensive compendium of research about Multiple sclerosis and cannabis compiled by calgarycmmc.com
- 'Cannabis and Multiple Sclerosis—The Way Forward' at FrontiersIn.org
- https://herb.co/news/health/marijuana-and-ms
- https://www.learngreenflower.com/articles/440/treating-multiple-sclerosis-with-cannabis
Seizures and cannabis
Traumatic brain injury and cannabis
Cannabis can help in healing from TBI
- 'Cannabis Therapeutics and the Future of Neurology: Cannabis and Traumatic Brain Injury (TBI)/Chronic Traumatic Encephalopathy (CTE)', a 2018 perspective article
Administering cannabis
There are various other ways to administer cannabis methods besides smoking it:
Vaping cannabis

- Vaping (short for vaporizing), a method where the plant material is heated hot enough for the cannabinoids to become gaseous but cold enough that the plant matter does not combust and thus avoiding the carcinogens that come from burning the plant matter. Vaping is also the preferred method to consume concentrates.
Links
Oral cannabis

- Edibles, tinctures and cannabis oil may be administered orally. Cannabinoids are soluble to alcohol and to fat and cannabis can be infused into many forms of edibles, but the problem is with efficiency as your stomach acids will destroy a lot of the cannabinoids.
Links
- Harvard Health Blog on edibles
- Do Edibles Give You A Different High Than Smoking? article at tonic.vice.com
- Herb.co article on cannabis tinctures
- Herb.co guide to making cannabis oil (word of caution: the procedure is dangerous as there are risks of explosion if done wrong, so don't be toasted outta it if and when you decide to make cannabis oil)
Rectal cannabis
- Rectal - some doctors recommend taking cannabis rectally as this is method of administering allows you to take very large doses efficiently.[20]
Links
- https://hightimes.com/health/science/doctors-orders-put-marijuana-in-your-butt-dont-smoke-it/
- https://www.huffingtonpost.ca/2017/03/05/rectal-marijuana_n_15178784.html
- https://inhalemd.com/massachusetts-medical-cannabis-guide/how-to-make-cannabis-suppositories-at-home/
- https://www.leafly.com/news/health/dont-laugh-rectal-suppositories-future-medicinal-cannabis
- https://www.medicaldaily.com/rectal-medical-marijuana-effective-safer-smoking-weed-suppository-wont-be-413077
- https://www.rxleaf.com/tush-kush-what-you-need-to-know-about-suppositories
Topical cannabis
- Topicals - for some skin affecting conditions this is a good way to administer the medicine. Many skin condition sufferers praise the combination of cannabis and coconut oil to make a topical to apply to the affected skin.
Right under the belly button there is a gland called Pechoti, which some say is a very good way to administer medical cannabis. Naval administration of medicine is a method used by the ancient Ayurvedic medicine.
Links
Dandelion
Dandelion root concentrates found effective against chemo-resistant melanoma and leukemia.[21]
"Since the commencement of this project, we have been able to successfully assess the effect of a simple water extract of dandelion root in various human cancer cell types, in the lab and we have observed its effectiveness against human T cell leukemia, chronic myelomonocytic leukemia, pancreatic and colon cancers, with no toxicity to non-cancer cells. Furthermore, these efficacy studies have been confirmed in animal models (mice) that have been transplanted with human colon cancer cells."[22]
- Dandelion root ‘found to kill’ chemo-resistant melanoma and leukemia a 2019 article at GetHolisticHealth.com
- The Dandelion Root Project at University of Windsor, Ontario since 2009
Elderberries
Elderberries (or Elder) belong to the genus w:Sambucus and may be useful for various kinds of flu.
- https://www.getholistichealth.com/78315/elderberry-eliminate-cold-flu/ lists a few studies that found it effective
- https://nccih.nih.gov/health/euroelder just states that more studies must be done to determine if it helps with flus
Ginger


11 health benefits of ginger at healthline.com (with sources)
- Ginger contains w:Gingerol, a substance with powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties.[23]
- Ginger can treat many forms of nausea, especially morning sickness and chemo-induced nausea[23]
- Ginger may reduce muscle pain and soreness [23]
- Ginger can help with w:osteoarthritis [23]
- Ginger may lower blood sugars [23]
- Ginger can help treat chronic indigestion [23]
- Ginger powder may significantly reduce menstrual pain [23]
- Ginger may lower cholesterol levels [23]
- Ginger contains gingerol, which may help to prevent cancers [23]
- Ginger may improve brain functioning and protect against Alzheimer's disease [23]
- Gingerol can help lower risk of infections [23]
Pineapple

Pineapple fruit and it's stem contain Bromelain, an enzyme with anti-cough properties.
In vitro and in vivo studies demonstrate that bromelain exhibits various fibrinolytic, antiedematous, antithrombotic, and anti-inflammatory activities.[24] Bromelain accounts for many therapeutic benefits like the treatment of angina pectoris, bronchitis, sinusitis, surgical trauma, and thrombophlebitis, debridement of wounds, and enhanced absorption of drugs, particularly antibiotics.[24]
Spirulina
Spirulina is a biomass of a (blue-green algae) that can be consumed by humans and other animals. The two species are Arthrospira platensis and A. maxima. ( Wikipedia )
Spirulina is extremely high in protein, contains an almost perfect balance of Omega-3 to Omega-6, and is rich in the following minerals: iron, copper, calcium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorous, selenium and zinc. It also contains high levels of vitamin A, C, E, K, B6, folate, niacin, pantothenic acid, riboflavin and thiamin. [25]
Spirulina has been found to help against [25]
- HIV/AIDS
- Beneficial for Type 2 Diabetes by regulating blood sugar levels and helping with w:blood lipids composition
- Candida
- Cancers because of its high C-phycocyanin, a powerful antioxidant and anti-inflammatory substance and anti-cancer properties
- Binding to w:heavy metals and therefore aiding in their removal
- Heart disease
- Allergies
Stevia
Stevia is a sweetener and sugar substitute extracted from the leaves of the plant species Stevia rebaudiana, native to Brazil and Paraguay.
Stevia and Lyme disease
Lyme disease also known as Lyme borreliosis, is an infectious disease caused by a bacterium named Borrelia spread by ticks.
Stevia works against the Lyme disease.[26]
Links about stevia and Lyme disease
- https://www.healthspiritbody.com/lyme-disease-treatment/
- https://livelovefruit.com/stevia-kills-lyme-disease/
Tea
Thyme

Thyme contains w:thymol, which is a natural antibiotic. Oil of thyme, the essential oil of common thyme (w:Thymus vulgaris), contains 20–54% thymol and other substances. (Wikipedia)
- 'Thyme essential oil found to cure just about any infection of the throat and lungs' at GetHolisticHealth.com (2019 article)
Turmeric
Turmeric contains curcumin, a curcuminoid.
Cancers and turmeric
Curcumin has been found to have anti-cancer properties. Curcumin interferes with cancer via multiple cell signaling pathways, including cell cycle, apoptosis, proliferation, survival, invasion, angiogenesis, metastasis and inflammation[27].
- Study: Curcumin and Cancer Cells: How Many Ways Can Curry Kill Tumor Cells Selectively?
- General info: Turmeric and cancers article by Cancer Research UK
See also: Cancers and cannabis (intra-article link)
Alzheimer's and turmeric
- 'Optimized Turmeric Extract Reduces β-Amyloid and Phosphorylated Tau Protein Burden in Alzheimer’s Transgenic Mice' suggests that turmeric may be useful for Alzheimer's sufferers as it has been shown to inhibit beta amyloid aggregation and secretation in mice.[28]
See also: Alzheimer's and cannabis (intra-article link)
Information sources on natural therapeutics
- Get Holistic Health publishes lots of articles on natural therapeutics, but also other topics.
- GreenMedinfo - The Science of Natural Healing
- HealthLine.com contains a myriad of information about different medical conditions and in addition to having info on conditions and natural therapeutics it also covers main stream medications
- https://herbalremediesbook.com/
- United Patients Group focuses on the healing potential of cannabis, but also carries stories on other natural therapeutics. United Patients Group also maintains and updates a directory of medical cannabis health care professionals and clinics.
References
- ↑ https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28270804
- ↑ https://www.hygiene-in-practice.com/publication/student-discovers-blackberry-antibiotic-for-multi-resistant-pathogens/
- ↑ https://wakeup-world.com/2014/09/08/the-endocannabinoid-system-and-how-thc-cures-cancer/
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 https://patients4medicalmarijuana.wordpress.com/2017/07/06/how-and-why-your-brain-makes-its-own-cannabinoids/
- ↑ 5.0 5.1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5685274/
- ↑ https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-59259-947-9_2
- ↑ 7.0 7.1 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Tetrahydrocannabinol
- ↑ Mechoulam, Raphael; Peters, Maximilian; Murillo-Rodriguez, Eric; Hanuš, Lumír O. (2007). "Cannabidiol – Recent Advances". Chemistry & Biodiversity. 4 (8): 1678–92. doi:10.1002/cbdv.200790147. PMID 17712814.
- ↑ 9.0 9.1 Cascio, MG; Gauson, LA; Stevenson, LA; Ross, RA; Pertwee, RG (2010). "Evidence that the plant cannabinoid cannabigerol is a highly potent α2-adrenoceptor agonist and moderately potent 5HT1A receptor antagonist". British Journal of Pharmacology. 159 (1): 129–41. doi:10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00515.x. PMC 2823359. PMID 20002104.
- ↑ Eberhard Breitmaier (2006). Terpenes: Flavors, Fragrances, Pharmaca, Pheromones. Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/9783527609949. ISBN 9783527609949.
- ↑ http://globalhealthtimes.com/2019/03/06/scientists-are-making-thc-and-cbd-in-a-lab-without-growing/
- ↑ 12.0 12.1 12.2 12.3 12.4 12.5 12.6 12.7 https://livelovefruit.com/8-non-marijuana-plants-contain-cannabinoids/
- ↑ https://www.newsweek.com/medical-marijuana-moss-plant-acts-thc-cannabis-1184661
- ↑ 14.0 14.1 14.2 14.3 https://herb.co/news/health/cannabis-kills-cancer/
- ↑ https://herb.co/news/health/world-first-cannabis-chemotherapy/
- ↑ https://www.medicinalcannabis.nsw.gov.au/clinical-trials/chemotherapy-trial
- ↑ https://www.medicaldaily.com/marijuana-just-might-help-cure-one-deadliest-forms-brain-cancer-410947
- ↑ http://wphealth.cc/2018/10/11/fda-approves-cannabis-for-brain-cancer-treatment/
- ↑ https://www.theguardian.com/uk/1998/dec/24/monarchy.ameliagentleman
- ↑ https://hightimes.com/health/science/doctors-orders-put-marijuana-in-your-butt-dont-smoke-it/
- ↑ https://www.getholistichealth.com/79015/dandelion-root-kill-melanoma-leukemia/
- ↑ http://www.uwindsor.ca/dandelionrootproject/
- ↑ 23.00 23.01 23.02 23.03 23.04 23.05 23.06 23.07 23.08 23.09 23.10 https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/11-proven-benefits-of-ginger
- ↑ 24.0 24.1 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3529416/
- ↑ 25.0 25.1 https://livelovefruit.com/top-spirulina-benefits/
- ↑ https://www.healthspiritbody.com/lyme-disease-treatment/
- ↑ https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304383508002310
- ↑ https://www.ingentaconnect.com/content/ben/car/2012/00000009/00000004/art00012